Need to create a range of dates in an array for your Javascript project? It is stupidly simple with the date object, let Master Coffee walk you through some common examples – Let’s go!
CODE DOWNLOAD
I have released this under the MIT license, feel free to use it in your own project – Personal or commercial. Some form of credits will be nice though. 🙂
VIDEO TUTORIAL
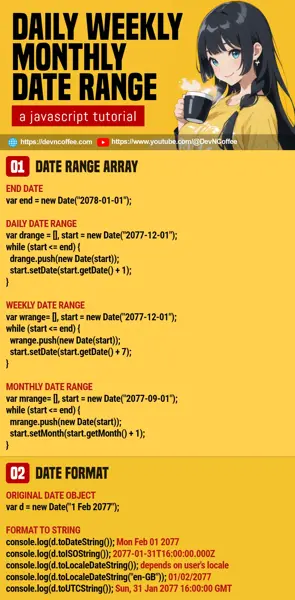
1) DAILY DATE RANGE
// (PART A) START & END DATE
var start = new Date("1 Feb 2077"),
end = new Date("1 Mar 2077");
// (PART B) CREATE DAILY DATE RANGE
var range = [];
while (start <= end) {
range.push(new Date(start));
start.setDate(start.getDate() + 1);
}
console.log(range);- First, define the
startandenddates.- If left blank,
new Date()will default to the current time on the device. - We can also provide the date/time in ISO format –
new Date("2077-12-01T12:34:56") - Finally, we can also pass in the “exact” year/month/day –
new Date(YEAR, MONTH, DAY). Take note,MONTH 0is January andMONTH 11is December.
- If left blank,
- Create the date range.
start.setDate(start.getDate() + 1)will increment the start date by one day.while (start <= end)loop until the start date hits the end date.- Take note, we push a new date object into the range –
range.push(new Date(start)). - This is confusing for beginners, but
range.push(start)will end up with an array of[1 Mar 2077, 1 Mar 2077, 1 Mar 2077, ...].
2) WEEKLY DATE RANGE
// (PART A) START & END DATE
var start = new Date("1 Feb 2077"),
end = new Date("1 Mar 2077");
// (PART B) CREATE WEEKLY DATE RANGE
var range = [];
while (start <= end) {
range.push(new Date(start));
start.setDate(start.getDate() + 7);
}
console.log(range);Look no further, this is the same process as the previous example – Except that we increment 7 days (1 week) “every cycle” now.
3) MONTHLY DATE RANGE
// (PART A) START & END DATE
var start = new Date("1 Nov 2077"),
end = new Date("1 Feb 2078");
// (PART B) CREATE MONTHLY DATE RANGE
var range = [];
while (start <= end) {
range.push(new Date(start));
start.setMonth(start.getMonth() + 1);
}
console.log(range);Once again, this is the same loop. But take note, we increment by one month “per cycle” now – start.setMonth(start.getMonth() + 1)
4) DATE RANGE USING UNIX TIMESTAMP
// (PART A) START & END DATE
var start = new Date("1 Jan 2077"),
end = new Date("1 Feb 2077");
// (PART B) CREATE DAILY DATE RANGE
var range = [];
// 1 day = 86400000 microseconds
for (let unix = start.getTime(); unix <= end.getTime(); unix += 86400000) {
range.push(new Date(unix));
}
console.log(range);This is an alternative way of using the Unix Timestamp to create a range of dates.
- Begin with the start and end dates as usual.
- For the beginners, a “Unix Timestamp” is simply the number of seconds that have elapsed since 1 Jan 1970 (UTC).
let unix = start.getTime()Get the start date in Unix Timestamp. But take note, Javascript returns the timestamp in microseconds.unix <= end.getTime()Loop until the start date hits the end date.unix += 86400000Increment by 1 day every cycle.
5) DATE FORMAT
// ORIGINAL DATE
var thedate = new Date("1 Feb 2077");
// Mon Feb 01 2077
console.log(thedate.toDateString());
// 2077-01-31T16:00:00.000Z
console.log(thedate.toISOString());
// USER'S LOCALE
console.log(thedate.toLocaleDateString());
// 01/02/2077
console.log(thedate.toLocaleDateString("en-GB"));
// Sun, 31 Jan 2077 16:00:00 GMT
console.log(thedate.toUTCString());All of the above examples will create an array of date objects. If you need to format to a date string, there are several “date to string” functions you can use:
toDateString()To a “human readable” format ofDAY MMM DD YYYY.toISOString()To standard ISO 8601 –YYYY-MM-DDTHH:MM:SS.SSSZtoLocaleDateString()There are several ways to use this, I will recommend reading through the documentation.toUTCString()Take note,new Date()will be based on the timezone set on the device. This will convert the date object to a string and in UTC.
THE END – FOR EVERY N DAYS, M WEEKS, O MONTHS, ETC…
That’s all for this short tutorial and sharing. For the beginners who are still confused, just add the number of days/months/years accordingly for a range of every N days/M weeks/O years. For example:
- Every 2 days –
start.setDate(start.getDate() + 2) - Every bi-weekly –
start.setDate(start.getDate() + 14) - Every quarterly –
start.setMonth(start.getMonth() + 3) - Every year
start.setYear(start.getYear() + 1)
CHEAT SHEET